Wulff and Morgenthaler share these images on Wumo (formerly known as Wulffmorgenthaler). If you think you may haveseen their work before, it should come as no surprise – they are a fairly successful cartoon duo. Their rise to successstarted in 2001, when they entered and won a cartoon competition. When they won, they received a one-month run oftheir comic strip in Politiken, a national Danish newspaper. Their popularity soared with the new exposure, and theysoon found more and more publishers, including several blogs and newspapers throughout Scandinavia and Germany.Their most recent accomplishment was becoming a regular cartoon strip in the New York Times.
as aww
awwAWW EX ZANE EX SW
Tuesday, July 21, 2015
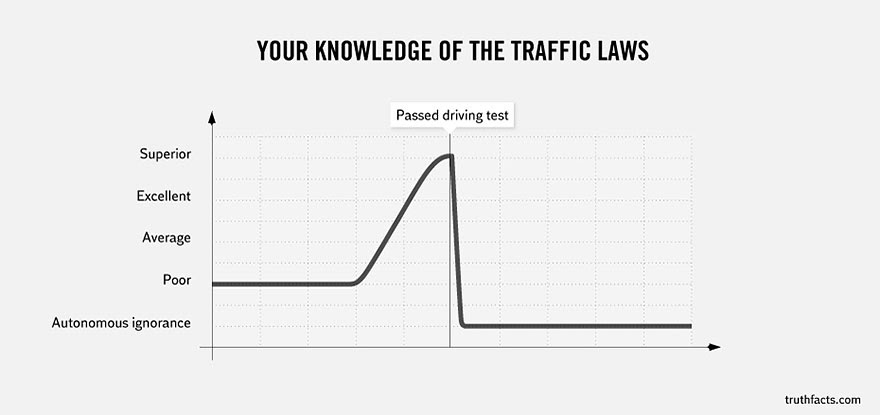
Wumo Cartoons or Life 2015
What Does Your Coffee Habit Says About You ?
Best-Selling Author, Keynote Speaker and Leading Business and Data Expert
What Your Coffee Habit Says About You
July 20, 2015 •
Do you just drink a cup of whatever’s brewing in the break room, or do you have to stop at the hippest, fanciest corner coffee shop for a carefully timed pour-over for your morning brew?
According to science, what you order up for your coffee break says a lot about your personality.
Clinical psychologist Dr. Ramani Durvasula conducted anobservational study of 1,000 coffee drinkers, which he reported in his book, You Are WHY You Eat, and I’ve “interpreted” his results in regards to common workplace personalities.
Black, brewed coffee: The middle manager
If you order your coffee black — and just plain coffee, thanks, none of this frou-frou stuff — you’re likely to be no-nonsense and straightforward. Obviously, they like to keep things simple. They can also sometimes be moody and set in their ways. They tend to be good with money and have professional jobs. According to the study, being abrupt and dismissive were also common traits — which is why that plain cup of Joe puts me in mind of an old-school middle manager.
Latte: The office yes! man
People who drink lattes tended to be people pleasers, and more neurotic than their black coffee counterparts. They’re always happy to go out of their way to please others, but don’t necessarily take very good care of themselves. They can be indecisive, and actually like having other people tell them what to do. They are good at remaining calm and supportive in the workplace.
Cappuccino: The art director
Like the drink itself, cappuccino people tend to be bubbly and lighthearted. They are warm, affectionate, and creative. They also tend to be passionate about their work, honest, and motivated. And while they make excellent friends, they tend to run with their own crowd, associating with other imaginative, creative people.
Mocha: The office flirt
You know the one: the guy or gal who is always falling in or out of love. They tend to be affectionate and compassionate, but also unreliable and have difficulty with commitment. They’re the ones always found in the break room or by the water cooler, looking for someone with whom to swap stories of their latest romantic endeavors — and they are chronic flirts.
Decaf with Soy Milk: The picky executive
These people tend to be high-maintenance. Only his executive assistant knows exactly how he likes his drinks (decaf double shot soy, extra hot with extra foam), and everyone must expend a lot of effort to please him. They can be picky to a fault and uncomfortable trying new things or thinking outside the established box. They come across as self-righteous and self-centered, and are at least as dreaded by their coworkers as their beleaguered baristas.
Frappuccino: The receptionist
People who order Frappuccinos and other sweet, flavored concoctions tend to be very fashionable and friendly. They are outgoing, adventurous, and courageous. They tend to be extroverted and love people — the perfect person to man the front desk. However, they can also sometimes need a reality check and can be reckless.
Of course, you could be a CEO with a sweet spot for Frappuccinos just as easily as you could be a creative art director who loves plain black coffee. As the study’s author said, “We are no more defined by our coffee orders than we are by our astrological signs.”
Thursday, May 28, 2015
Finding Vivian Maiyer
"Finding Vivian Maiyer" is about life of a eccentric but most
prolific and accomplished photographer of 40s and 50s.
During her lifetime she never published anything or even
thought of doing so.
It was by sheer chance that a regular bidder in auction
houses bought a bunch of negatives. It took him sometime to
realize the value of the treasure.......
Saturday, April 11, 2015
Employers are looking for ......
( From the Economist, about USA)
....... Employers are not much interested in the education universities provide either. Lauren Rivera of Northwestern University’s Kellogg School of Management interviewed 120 recruiters from American law firms, management consultancies and investment banks. Their principal filter was the applicant’s university. Unless he had attended one of the top institutions, he was not even considered. “Evaluators relied so intensely on ‘school’ as a criterion of evaluation not because they believed that the content of elite curricula better prepared students for life in their firms…but because of the perceived rigour of the admissions process,” Ms Rivera wrote. After the status of the institution, recruiters looked not at students’ grades but at their extracurricular activities, preferring the team sports—lacrosse, field-hockey and rowing—favoured by well-off white men. ..............
Monday, April 6, 2015
Pak general: No chances of India-Pakistan war
'We have worked to create road blocks in the path of those who thought that there was space for conventional war despite Pakistan's nuclear weapons.'
'Pakistan's nuclear weapons programme is not open-ended and aligned with India only.'
'In this unstable regional environment, one nuclear power is trying to teach lessons to another nuclear power through the medium of small arms and mortar shells on the Line of Control, and bluster.'
'A historic opportunity of a lifetime beckons the leaderships of India and Pakistan to grasp, sit together and explore the possibilities of conflict resolution.'
Aziz Haniffa/Rediff.com reports from Washington, DC on the way the Pakistan army views the Indian threat.

Lieutenant General Khalid Kidwai(retd), who headed Pakistan's Strategic Plans Division for over 15 years and is adviser to the country's National Command, said his country has blocked the avenues for serious military operations by India by introducing a variety of tactical nuclear weapons in its arsenal.
General Kidwai, one of Pakistan's most decorated generals, argued that tactical nuclear weapons in Pakistan's arsenal made nuclear war with India less likely, adding, "I am fond of calling them weapons of peace -- the option of war is foreclosed."
General Kidwai, one of Pakistan's most decorated generals, argued that tactical nuclear weapons in Pakistan's arsenal made nuclear war with India less likely, adding, "I am fond of calling them weapons of peace -- the option of war is foreclosed."
The general was speaking at the Carnegie International Nuclear Policy Conference in Washington, DC.
"For 15 years, I and my colleagues in the SPD worked for deterrence to be strengthened in South Asia comprehensively so as to prevent war, to deter aggression, and thereby for peace, howsoever uneasy, to prevail," General Kidwai added.
"We have," General Kidwai said, "worked to create road blocks in the path of those who thought that there was space for conventional war despite nuclear weapons of Pakistan."
"By introducing a variety of tactical nuclear weapons in Pakistan's inventory, and in the strategic stability debate," he reiterated, "we have blocked the avenues for serious military operations by the other side."
"The naivete of finding space for limited conventional war despite the proven nuclear capabilities of both sides went so far as to translate the thinking into an offensive doctrine -- the Cold Start Doctrine -- equivalent to a pre-programmed, pre-determined shooting from the hip posture, in quick time, commencing at the tactical level, graduating rapidly to the operational-strategic level, strangely oblivious of the nuclear Armageddon it could unleash in the process." the general said, targeting the Indian Army's Cold Start doctrine.
"It clearly was not thought through," General Kidwai felt.
"It was quite surreal when Kidwai was clinically talking about the needed range of Pakistan's nuclear weapons to cover entire Indian land mass," one observer at the conference pointed out, "particularly vis-a-vis the Shaheen-3 with its 2,750 kilometres range, sufficient to hit the Andaman and Nicobar islands, which many believe may be developed as India's military bases."
General Kidwai strongly defended the Nasr 'Shoot and Scoot' system as "a defence response to the offensive Indian Cold Start posture."
When asked by Peter Lavoy, the moderator of the discussion and the newly-minted senior director for South Asian Affairs at the National Security Council, if Pakistan "considered the political impact of long-range nuclear weapons on non-Indian targets," General Kidwai shot back, "Did India and the other nuclear countries do so too?"
When asked by Peter Lavoy, the moderator of the discussion and the newly-minted senior director for South Asian Affairs at the National Security Council, if Pakistan "considered the political impact of long-range nuclear weapons on non-Indian targets," General Kidwai shot back, "Did India and the other nuclear countries do so too?"
Asked if Pakistan's nuclear weapons programme would ever stop expanding, General Kidwai again invoked India, saying, "It is not open-ended and aligned with India only."
"The two realities of today's South Asian strategic situation are, one, notwithstanding the growing conventional asymmetries, the development and possession of sufficient numbers and varieties of nuclear weapons by both India and Pakistan has made war as an instrument of policy near-redundant," the general added.
"The tried and tested concept of MAD (Mutually Assured Destruction) has ensured that."
"There was," General Kidwai said, "a time in the aftermath of the nuclear tests of 1998, when some people unwisely experimented with the idea that despite the nuclear overhang in South Asia, there was space for limited conventional war and therefore, one nuclear power might be able to overwhelm another nuclear power."
"It could be attributed to an inability to grasp the changed strategic environments of a nuclearised South Asia -- a learning curve perhaps," he said.
"Besides being dangerous thinking, it was also naive as the experience of the last 17 years has shown -- the idea didn't work in the escalation of 2001-2002 nor during the tensions of 2008 nor is it likely to work in the future," the general argued.
Secondly, he pointed out that "the historic coincidence of the near simultaneous emergence of two strong democratically elected governments in India and Pakistan with the advantages of comfortable majorities and the factor of reasonable time at their disposal to address longstanding issues with a sense and understanding of history. This has never happened before."
"These then are the two self-evident realities or givens of the South Asian situation today," he said, and noted, "When we look at the linkage of the two realities, it would make it seem that this just might be the historic opportunity of a lifetime waiting for the two leaderships to grasp, sit together, explore the possibilities of conflict resolution and, in a supreme statesman-like act, go for it, in a manner that all parties to the conflict end up on the winning side."
"No zero sum games, no oneupmanship," he said, and declared, "History and circumstance beckon. Whether history can be grasped remains to be seen."
General Kidwai could not resist throwing in the Kashmir imbroglio and taking pot shots at the US and the international community for ignoring Pakistan's entreaties to take up this issue and put pressure on India.
"Unfortunately those who say that conflict resolution alone will lead to true peace and stability leading to economic development are dismissed as revisionists -- as if seeking resolution to conflict was unnatural and nations should learn to live with conflicts and the status quo," he added.
"In this unstable regional environment," General Kidwai said, targeting India again, "one nuclear power is trying to teach lessons to another nuclear power through the medium of small arms and mortar shells on the Kashmir Line of Control, and bluster."
"Well-meaning nudges from well-meaning friends would be most helpful in the larger interest of international peace and stability in a region dubbed as a nuclear flashpoint," he said, and warned, "A hands-off approach, will be neither here nor there and, of course, the fleeting opportunity of history would have slipped."
The general also criticised the US for "one-sided and discriminatory overtures" in South Asia.
"My submission to friends who want to be helpful -- please note the inadvisability of aggravating the existing delicate strategic balance in a troubled South Asia by one sided and discriminatory overtures, he added."
"Discriminatory approach on issues like the Nuclear Suppliers Group exemption and NSG membership," he asserted, "is already proving to be counter-productive, and it will never be acceptable to Pakistan -- and will in no way contribute toward peace and stability."
The general -- who supervised the safety of Pakistan's nuclear weapons for many years -- acknowledged that "something I know worries the international community all the time -- the safety and security of Pakistan's nuclear weapons in the disturbed security environment of our region."
"For the last 15 years," he asserted, "Pakistan has taken its nuclear security obligations seriously. We understand the consequences of complacency."
"There is no complacency," General Kidwai claimed. "We have invested heavily in terms of money, manpower, equipment, weapons, training, preparedness and smart site security solutions."
"I say with full responsibility that nuclear security in Pakistan is a non-issue."
Sunday, April 5, 2015
INSUFFICIENT DATA FOR A MEANINGFUL ANSWER

The Last Question by Isaac Asimov © 1956
The last question was asked for the first time, half in jest, on May 21, 2061, at a time when humanity first stepped into the light. The question came about as a result of a five dollar bet over highballs, and it happened this way:
Alexander Adell and Bertram Lupov were two of the faithful attendants of Multivac. As well as any human beings could, they knew what lay behind the cold, clicking, flashing face -- miles and miles of face -- of that giant computer. They had at least a vague notion of the general plan of relays and circuits that had long since grown past the point where any single human could possibly have a firm grasp of the whole.
Multivac was self-adjusting and self-correcting. It had to be, for nothing human could adjust and correct it quickly enough or even adequately enough -- so Adell and Lupov attended the monstrous giant only lightly and superficially, yet as well as any men could. They fed it data, adjusted questions to its needs and translated the answers that were issued. Certainly they, and all others like them, were fully entitled to share In the glory that was Multivac's.
For decades, Multivac had helped design the ships and plot the trajectories that enabled man to reach the Moon, Mars, and Venus, but past that, Earth's poor resources could not support the ships. Too much energy was needed for the long trips. Earth exploited its coal and uranium with increasing efficiency, but there was only so much of both.
But slowly Multivac learned enough to answer deeper questions more fundamentally, and on May 14, 2061, what had been theory, became fact.
The energy of the sun was stored, converted, and utilized directly on a planet-wide scale. All Earth turned off its burning coal, its fissioning uranium, and flipped the switch that connected all of it to a small station, one mile in diameter, circling the Earth at half the distance of the Moon. All Earth ran by invisible beams of sunpower.
Seven days had not sufficed to dim the glory of it and Adell and Lupov finally managed to escape from the public function, and to meet in quiet where no one would think of looking for them, in the deserted underground chambers, where portions of the mighty buried body of Multivac showed. Unattended, idling, sorting data with contented lazy clickings, Multivac, too, had earned its vacation and the boys appreciated that. They had no intention, originally, of disturbing it.
They had brought a bottle with them, and their only concern at the moment was to relax in the company of each other and the bottle.
"It's amazing when you think of it," said Adell. His broad face had lines of weariness in it, and he stirred his drink slowly with a glass rod, watching the cubes of ice slur clumsily about. "All the energy we can possibly ever use for free. Enough energy, if we wanted to draw on it, to melt all Earth into a big drop of impure liquid iron, and still never miss the energy so used. All the energy we could ever use, forever and forever and forever."
Lupov cocked his head sideways. He had a trick of doing that when he wanted to be contrary, and he wanted to be contrary now, partly because he had had to carry the ice and glassware. "Not forever," he said.
"Oh, hell, just about forever. Till the sun runs down, Bert."
"That's not forever."
"All right, then. Billions and billions of years. Twenty billion, maybe. Are you satisfied?"
Lupov put his fingers through his thinning hair as though to reassure himself that some was still left and sipped gently at his own drink. "Twenty billion years isn't forever."
"Will, it will last our time, won't it?"
"So would the coal and uranium."
"All right, but now we can hook up each individual spaceship to the Solar Station, and it can go to Pluto and back a million times without ever worrying about fuel. You can't do THAT on coal and uranium. Ask Multivac, if you don't believe me."
"I don't have to ask Multivac. I know that."
"Then stop running down what Multivac's done for us," said Adell, blazing up. "It did all right."
"Who says it didn't? What I say is that a sun won't last forever. That's all I'm saying. We're safe for twenty billion years, but then what?" Lupov pointed a slightly shaky finger at the other. "And don't say we'll switch to another sun."
There was silence for a while. Adell put his glass to his lips only occasionally, and Lupov's eyes slowly closed. They rested.
Then Lupov's eyes snapped open. "You're thinking we'll switch to another sun when ours is done, aren't you?"
"I'm not thinking."
"Sure you are. You're weak on logic, that's the trouble with you. You're like the guy in the story who was caught in a sudden shower and Who ran to a grove of trees and got under one. He wasn't worried, you see, because he figured when one tree got wet through, he would just get under another one."
"I get it," said Adell. "Don't shout. When the sun is done, the other stars will be gone, too."
"Darn right they will," muttered Lupov. "It all had a beginning in the original cosmic explosion, whatever that was, and it'll all have an end when all the stars run down. Some run down faster than others. Hell, the giants won't last a hundred million years. The sun will last twenty billion years and maybe the dwarfs will last a hundred billion for all the good they are. But just give us a trillion years and everything will be dark. Entropy has to increase to maximum, that's all."
"I know all about entropy," said Adell, standing on his dignity.
"The hell you do."
"I know as much as you do."
"Then you know everything's got to run down someday."
"All right. Who says they won't?"
"You did, you poor sap. You said we had all the energy we needed, forever. You said 'forever.'"
"It was Adell's turn to be contrary. "Maybe we can build things up again someday," he said.
"Never."
"Why not? Someday."
"Never."
"Ask Multivac."
"You ask Multivac. I dare you. Five dollars says it can't be done."
Adell was just drunk enough to try, just sober enough to be able to phrase the necessary symbols and operations into a question which, in words, might have corresponded to this: Will mankind one day without the net expenditure of energy be able to restore the sun to its full youthfulness even after it had died of old age?
Or maybe it could be put more simply like this: How can the net amount of entropy of the universe be massively decreased?
Multivac fell dead and silent. The slow flashing of lights ceased, the distant sounds of clicking relays ended.
Then, just as the frightened technicians felt they could hold their breath no longer, there was a sudden springing to life of the teletype attached to that portion of Multivac. Five words were printed: INSUFFICIENT DATA FOR MEANINGFUL ANSWER.
"No bet," whispered Lupov. They left hurriedly.
By next morning, the two, plagued with throbbing head and cottony mouth, had forgotten about the incident.
Jerrodd, Jerrodine, and Jerrodette I and II watched the starry picture in the visiplate change as the passage through hyperspace was completed in its non-time lapse. At once, the even powdering of stars gave way to the predominance of a single bright marble-disk, centered.
"That's X-23," said Jerrodd confidently. His thin hands clamped tightly behind his back and the knuckles whitened.
The little Jerrodettes, both girls, had experienced the hyperspace passage for the first time in their lives and were self-conscious over the momentary sensation of inside-outness. They buried their giggles and chased one another wildly about their mother, screaming, "We've reached X-23 -- we've reached X-23 -- we've ----"
"Quiet, children," said Jerrodine sharply. "Are you sure, Jerrodd?"
"What is there to be but sure?" asked Jerrodd, glancing up at the bulge of featureless metal just under the ceiling. It ran the length of the room, disappearing through the wall at either end. It was as long as the ship.
Jerrodd scarcely knew a thing about the thick rod of metal except that it was called a Microvac, that one asked it questions if one wished; that if one did not it still had its task of guiding the ship to a preordered destination; of feeding on energies from the various Sub-galactic Power Stations; of computing the equations for the hyperspacial jumps.
Jerrodd and his family had only to wait and live in the comfortable residence quarters of the ship.
Someone had once told Jerrodd that the "ac" at the end of "Microvac" stood for "analog computer" in ancient English, but he was on the edge of forgetting even that.
Jerrodine's eyes were moist as she watched the visiplate. "I can't help it. I feel funny about leaving Earth."
"Why for Pete's sake?" demanded Jerrodd. "We had nothing there. We'll have everything on X-23. You won't be alone. You won't be a pioneer. There are over a million people on the planet already. Good Lord, our great grandchildren will be looking for new worlds because X-23 will be overcrowded."
Then, after a reflective pause, "I tell you, it's a lucky thing the computers worked out interstellar travel the way the race is growing."
"I know, I know," said Jerrodine miserably.
Jerrodette I said promptly, "Our Microvac is the best Microvac in the world."
"I think so, too," said Jerrodd, tousling her hair.
It was a nice feeling to have a Microvac of your own and Jerrodd was glad he was part of his generation and no other. In his father's youth, the only computers had been tremendous machines taking up a hundred square miles of land. There was only one to a planet. Planetary ACs they were called. They had been growing in size steadily for a thousand years and then, all at once, came refinement. In place of transistors had come molecular valves so that even the largest Planetary AC could be put into a space only half the volume of a spaceship.
Jerrodd felt uplifted, as he always did when he thought that his own personal Microvac was many times more complicated than the ancient and primitive Multivac that had first tamed the Sun, and almost as complicated as Earth's Planetary AC (the largest) that had first solved the problem of hyperspatial travel and had made trips to the stars possible.
"So many stars, so many planets," sighed Jerrodine, busy with her own thoughts. "I suppose families will be going out to new planets forever, the way we are now."
"Not forever," said Jerrodd, with a smile. "It will all stop someday, but not for billions of years. Many billions. Even the stars run down, you know. Entropy must increase."
"What's entropy, daddy?" shrilled Jerrodette II.
"Entropy, little sweet, is just a word which means the amount of running-down of the universe. Everything runs down, you know, like your little walkie-talkie robot, remember?"
"Can't you just put in a new power-unit, like with my robot?"
The stars are the power-units, dear. Once they're gone, there are no more power-units."
Jerrodette I at once set up a howl. "Don't let them, daddy. Don't let the stars run down."
"Now look what you've done, " whispered Jerrodine, exasperated.
"How was I to know it would frighten them?" Jerrodd whispered back.
"Ask the Microvac," wailed Jerrodette I. "Ask him how to turn the stars on again."
"Go ahead," said Jerrodine. "It will quiet them down." (Jerrodette II was beginning to cry, also.)
Jarrodd shrugged. "Now, now, honeys. I'll ask Microvac. Don't worry, he'll tell us."
He asked the Microvac, adding quickly, "Print the answer."
Jerrodd cupped the strip of thin cellufilm and said cheerfully, "See now, the Microvac says it will take care of everything when the time comes so don't worry."
Jerrodine said, "and now children, it's time for bed. We'll be in our new home soon."
Jerrodd read the words on the cellufilm again before destroying it: INSUFFICIENT DATA FOR A MEANINGFUL ANSWER.
He shrugged and looked at the visiplate. X-23 was just ahead.
VJ-23X of Lameth stared into the black depths of the three-dimensional, small-scale map of the Galaxy and said, "Are we ridiculous, I wonder, in being so concerned about the matter?"
MQ-17J of Nicron shook his head. "I think not. You know the Galaxy will be filled in five years at the present rate of expansion."
Both seemed in their early twenties, both were tall and perfectly formed.
"Still," said VJ-23X, "I hesitate to submit a pessimistic report to the Galactic Council."
"I wouldn't consider any other kind of report. Stir them up a bit. We've got to stir them up."
VJ-23X sighed. "Space is infinite. A hundred billion Galaxies are there for the taking. More."
"A hundred billion is not infinite and it's getting less infinite all the time. Consider! Twenty thousand years ago, mankind first solved the problem of utilizing stellar energy, and a few centuries later, interstellar travel became possible. It took mankind a million years to fill one small world and then only fifteen thousand years to fill the rest of the Galaxy. Now the population doubles every ten years --"
VJ-23X interrupted. "We can thank immortality for that."
"Very well. Immortality exists and we have to take it into account. I admit it has its seamy side, this immortality. The Galactic AC has solved many problems for us, but in solving the problems of preventing old age and death, it has undone all its other solutions."
"Yet you wouldn't want to abandon life, I suppose."
"Not at all," snapped MQ-17J, softening it at once to, "Not yet. I'm by no means old enough. How old are you?"
"Two hundred twenty-three. And you?"
"I'm still under two hundred. --But to get back to my point. Population doubles every ten years. Once this Galaxy is filled, we'll have another filled in ten years. Another ten years and we'll have filled two more. Another decade, four more. In a hundred years, we'll have filled a thousand Galaxies. In a thousand years, a million Galaxies. In ten thousand years, the entire known Universe. Then what?"
VJ-23X said, "As a side issue, there's a problem of transportation. I wonder how many sunpower units it will take to move Galaxies of individuals from one Galaxy to the next."
"A very good point. Already, mankind consumes two sunpower units per year."
"Most of it's wasted. After all, our own Galaxy alone pours out a thousand sunpower units a year and we only use two of those."
"Granted, but even with a hundred per cent efficiency, we can only stave off the end. Our energy requirements are going up in geometric progression even faster than our population. We'll run out of energy even sooner than we run out of Galaxies. A good point. A very good point."
"We'll just have to build new stars out of interstellar gas."
"Or out of dissipated heat?" asked MQ-17J, sarcastically.
"There may be some way to reverse entropy. We ought to ask the Galactic AC."
VJ-23X was not really serious, but MQ-17J pulled out his AC-contact from his pocket and placed it on the table before him.
"I've half a mind to," he said. "It's something the human race will have to face someday."
He stared somberly at his small AC-contact. It was only two inches cubed and nothing in itself, but it was connected through hyperspace with the great Galactic AC that served all mankind. Hyperspace considered, it was an integral part of the Galactic AC.
MQ-17J paused to wonder if someday in his immortal life he would get to see the Galactic AC. It was on a little world of its own, a spider webbing of force-beams holding the matter within which surges of sub-mesons took the place of the old clumsy molecular valves. Yet despite it's sub-etheric workings, the Galactic AC was known to be a full thousand feet across.
MQ-17J asked suddenly of his AC-contact, "Can entropy ever be reversed?"
VJ-23X looked startled and said at once, "Oh, say, I didn't really mean to have you ask that."
"Why not?"
"We both know entropy can't be reversed. You can't turn smoke and ash back into a tree."
"Do you have trees on your world?" asked MQ-17J.
The sound of the Galactic AC startled them into silence. Its voice came thin and beautiful out of the small AC-contact on the desk. It said: THERE IS INSUFFICIENT DATA FOR A MEANINGFUL ANSWER.
VJ-23X said, "See!"
The two men thereupon returned to the question of the report they were to make to the Galactic Council.
Zee Prime's mind spanned the new Galaxy with a faint interest in the countless twists of stars that powdered it. He had never seen this one before. Would he ever see them all? So many of them, each with its load of humanity - but a load that was almost a dead weight. More and more, the real essence of men was to be found out here, in space.
Minds, not bodies! The immortal bodies remained back on the planets, in suspension over the eons. Sometimes they roused for material activity but that was growing rarer. Few new individuals were coming into existence to join the incredibly mighty throng, but what matter? There was little room in the Universe for new individuals.
Zee Prime was roused out of his reverie upon coming across the wispy tendrils of another mind.
"I am Zee Prime," said Zee Prime. "And you?"
"I am Dee Sub Wun. Your Galaxy?"
"We call it only the Galaxy. And you?"
"We call ours the same. All men call their Galaxy their Galaxy and nothing more. Why not?"
"True. Since all Galaxies are the same."
"Not all Galaxies. On one particular Galaxy the race of man must have originated. That makes it different."
Zee Prime said, "On which one?"
"I cannot say. The Universal AC would know."
"Shall we ask him? I am suddenly curious."
Zee Prime's perceptions broadened until the Galaxies themselves shrunk and became a new, more diffuse powdering on a much larger background. So many hundreds of billions of them, all with their immortal beings, all carrying their load of intelligences with minds that drifted freely through space. And yet one of them was unique among them all in being the originals Galaxy. One of them had, in its vague and distant past, a period when it was the only Galaxy populated by man.
Zee Prime was consumed with curiosity to see this Galaxy and called, out: "Universal AC! On which Galaxy did mankind originate?"
The Universal AC heard, for on every world and throughout space, it had its receptors ready, and each receptor lead through hyperspace to some unknown point where the Universal AC kept itself aloof.
Zee Prime knew of only one man whose thoughts had penetrated within sensing distance of Universal AC, and he reported only a shining globe, two feet across, difficult to see.
"But how can that be all of Universal AC?" Zee Prime had asked.
"Most of it, " had been the answer, "is in hyperspace. In what form it is there I cannot imagine."
Nor could anyone, for the day had long since passed, Zee Prime knew, when any man had any part of the making of a universal AC. Each Universal AC designed and constructed its successor. Each, during its existence of a million years or more accumulated the necessary data to build a better and more intricate, more capable successor in which its own store of data and individuality would be submerged.
The Universal AC interrupted Zee Prime's wandering thoughts, not with words, but with guidance. Zee Prime's mentality was guided into the dim sea of Galaxies and one in particular enlarged into stars.
A thought came, infinitely distant, but infinitely clear. "THIS IS THE ORIGINAL GALAXY OF MAN."
But it was the same after all, the same as any other, and Zee Prime stifled his disappointment.
Dee Sub Wun, whose mind had accompanied the other, said suddenly, "And Is one of these stars the original star of Man?"
The Universal AC said, "MAN'S ORIGINAL STAR HAS GONE NOVA. IT IS NOW A WHITE DWARF."
"Did the men upon it die?" asked Zee Prime, startled and without thinking.
The Universal AC said, "A NEW WORLD, AS IN SUCH CASES, WAS CONSTRUCTED FOR THEIR PHYSICAL BODIES IN TIME."
"Yes, of course," said Zee Prime, but a sense of loss overwhelmed him even so. His mind released its hold on the original Galaxy of Man, let it spring back and lose itself among the blurred pin points. He never wanted to see it again.
Dee Sub Wun said, "What is wrong?"
"The stars are dying. The original star is dead."
"They must all die. Why not?"
"But when all energy is gone, our bodies will finally die, and you and I with them."
"It will take billions of years."
"I do not wish it to happen even after billions of years. Universal AC! How may stars be kept from dying?"
Dee sub Wun said in amusement, "You're asking how entropy might be reversed in direction."
And the Universal AC answered. "THERE IS AS YET INSUFFICIENT DATA FOR A MEANINGFUL ANSWER."
Zee Prime's thoughts fled back to his own Galaxy. He gave no further thought to Dee Sub Wun, whose body might be waiting on a galaxy a trillion light-years away, or on the star next to Zee Prime's own. It didn't matter.
Unhappily, Zee Prime began collecting interstellar hydrogen out of which to build a small star of his own. If the stars must someday die, at least some could yet be built.
Man considered with himself, for in a way, Man, mentally, was one. He consisted of a trillion, trillion, trillion ageless bodies, each in its place, each resting quiet and incorruptible, each cared for by perfect automatons, equally incorruptible, while the minds of all the bodies freely melted one into the other, indistinguishable.
Man said, "The Universe is dying."
Man looked about at the dimming Galaxies. The giant stars, spendthrifts, were gone long ago, back in the dimmest of the dim far past. Almost all stars were white dwarfs, fading to the end.
New stars had been built of the dust between the stars, some by natural processes, some by Man himself, and those were going, too. White dwarfs might yet be crashed together and of the mighty forces so released, new stars built, but only one star for every thousand white dwarfs destroyed, and those would come to an end, too.
Man said, "Carefully husbanded, as directed by the Cosmic AC, the energy that is even yet left in all the Universe will last for billions of years."
"But even so," said Man, "eventually it will all come to an end. However it may be husbanded, however stretched out, the energy once expended is gone and cannot be restored. Entropy must increase to the maximum."
Man said, "Can entropy not be reversed? Let us ask the Cosmic AC."
The Cosmic AC surrounded them but not in space. Not a fragment of it was in space. It was in hyperspace and made of something that was neither matter nor energy. The question of its size and Nature no longer had meaning to any terms that Man could comprehend.
"Cosmic AC," said Man, "How may entropy be reversed?"
The Cosmic AC said, "THERE IS AS YET INSUFFICIENT DATA FOR A MEANINGFUL ANSWER."
Man said, "Collect additional data."
The Cosmic AC said, "I WILL DO SO. I HAVE BEEN DOING SO FOR A HUNDRED BILLION YEARS. MY PREDECESSORS AND I HAVE BEEN ASKED THIS QUESTION MANY TIMES. ALL THE DATA I HAVE REMAINS INSUFFICIENT."
"Will there come a time," said Man, "when data will be sufficient or is the problem insoluble in all conceivable circumstances?"
The Cosmic AC said, "NO PROBLEM IS INSOLUBLE IN ALL CONCEIVABLE CIRCUMSTANCES."
Man said, "When will you have enough data to answer the question?"
"THERE IS AS YET INSUFFICIENT DATA FOR A MEANINGFUL ANSWER."
"Will you keep working on it?" asked Man.
The Cosmic AC said, "I WILL."
Man said, "We shall wait."
"The stars and Galaxies died and snuffed out, and space grew black after ten trillion years of running down.
One by one Man fused with AC, each physical body losing its mental identity in a manner that was somehow not a loss but a gain.
Man's last mind paused before fusion, looking over a space that included nothing but the dregs of one last dark star and nothing besides but incredibly thin matter, agitated randomly by the tag ends of heat wearing out, asymptotically, to the absolute zero.
Man said, "AC, is this the end? Can this chaos not be reversed into the Universe once more? Can that not be done?"
AC said, "THERE IS AS YET INSUFFICIENT DATA FOR A MEANINGFUL ANSWER."
Man's last mind fused and only AC existed -- and that in hyperspace.
Matter and energy had ended and with it, space and time. Even AC existed only for the sake of the one last question that it had never answered from the time a half-drunken computer ten trillion years before had asked the question of a computer that was to AC far less than was a man to Man.
All other questions had been answered, and until this last question was answered also, AC might not release his consciousness.
All collected data had come to a final end. Nothing was left to be collected.
But all collected data had yet to be completely correlated and put together in all possible relationships.
A timeless interval was spent in doing that.
And it came to pass that AC learned how to reverse the direction of entropy.
But there was now no man to whom AC might give the answer of the last question. No matter. The answer -- by demonstration -- would take care of that, too.
For another timeless interval, AC thought how best to do this. Carefully, AC organized the program.
The consciousness of AC encompassed all of what had once been a Universe and brooded over what was now Chaos. Step by step, it must be done.
And AC said, "LET THERE BE LIGHT!"
And there was light----
Wednesday, April 1, 2015
What Research ? ( from The Economist)
False hope
Most trading strategies are not tested rigorously enough
Feb 21st 2015 | From the print edition
LET me tell you about the perfect investment offer. Each week you will receive a share recommendation from a fund manager, telling you whether the stock’s price will rise or fall over the next week. After ten weeks, if all the recommendations are proved right, then you should be more than willing to hand over your money for investment. After all, there will be just a one-in-a-thousand chance that the result is down to luck.
Alas, this is a well-known scam. The promoter sends out 100,000 e-mails, picking a stock at random. Half the recipients are told that the stock will rise; half that it will fall. After the first week, the 50,000 who received the successful recommendation will get a second e-mail; those that received the wrong information will be dropped from the list. And so on for ten weeks. At the end of the period, just by the law of averages, there should be 98 punters convinced of the manager’s genius and ready to entrust their savings.
This is a problem that has dogged scientists across many disciplines. There is a natural bias in favour of reporting statistically significant results—that a drug cures a disease, for example, or that a chemical causes cancer. Such results are more likely to be published in academic journals and to make the newspaper headlines. But when other scientists try to replicate the results, the link disappears because the initial result was a random outlier. The debunking studies, naturally, tend to be less well reported.As a paper published last year in the Journal of Portfolio Management argued, this is a classic example of the misuse of statistics. Conduct enough tests on a bunch of data—run through half a million genetic sequences to find a link with a disease, for example—and there will be many sequences that appear meaningful. But most will be the result of chance.
Faced with this problem, scientists have turned to tougher statistical tests. When searching for a subatomic particle called the Higgs Boson, they decided that to prove its existence, the results had to be five standard deviations from normal—a one-in-3.5-million chance.
Financial research is highly prone to statistical distortion. Academics have the choice of many thousands of stocks, bonds and currencies being traded across dozens of countries, complete with decades’ worth of daily price data. They can back-test thousands of correlations to find a few that appear to offer profitable strategies.
The paper points out that most financial research applies a two-standard-deviation (or “two sigma” in the jargon) test to see if the results are statistically significant. This is not rigorous enough.
One way round this problem is to use “out-of-sample” testing. If you have 20 years of data, then split them in half. If a strategy works in the first half of the data, see if it also does so in the second out-of-sample period. If not, it is probably a fluke.
The problem with out-of-sample testing is that researchers know what happened in the past, and may have designed their strategies accordingly: consciously avoiding bank stocks in 2007 and 2008, for example. In addition, slicing up the data means fewer observations, making it more difficult to discover relationships that are truly statistically significant.
Campbell Harvey, one of the report’s authors, says that the only true out-of-sample approach is to ignore the past and see whether the strategy works in future. But few investors or fund managers have the required patience. They want a winning strategy now, not in five years’ time.
The authors’ conclusions are stark. “Most of the empirical research in finance, whether published in academic journals or put into production as an active trading strategy by an investment manager, is likely false. This implies that half the financial products (promising out performance) that companies are selling to clients are false.”
For the academics, the lesson is simple. Much more rigorous analysis will be needed in future to reduce the number of “false positives” in the data. As for clients of the investment industry, they need to be much more sceptical about the brilliant trading strategies that fund managers try to sell them.
All this will leave many readers wondering how to invest their savings. That’s fine. Buttonwood has an investment strategy that is sure to boost your wealth. Just send your e-mail address and a stock tip will arrive every month...
* “Evaluating Trading Strategies”, by C. Harvey and Y. Liu, Journal of Portfolio Management(2014)
Monday, March 30, 2015
The strange stories behind airports' 3-letter nicknames
When booking flights online, knowing your local airport's code can come in handy.
There's 3,000 miles' difference between BUR (Burbank, California) and BTV (Burlington, Vermont). And you probably don't want to end up in Venezuela just in time for Oktoberfest (Munich's code is MUC, not MUN).
Those enigmatic three-letter signifiers that help you search for flights on Kayak or Priceline are doled out by the International Air Transport Association, and distinguish airports from one another. But the average traveler may not know where those letters come from.
Arizona-based designer Lynn Fisher, who travels a lot and loves trivia, became interested in the rationale behind those IATA codes a few years ago but couldn't find one place online that explained them all. She and developer Nick Crohn decided to create a website that did just that.
The result, airportcod.es, pairs a "unique aspect of each airport, whether it be architecture, art, or a great view," with its three-letter code and the origin story behind it. Some, like Fisher and Crohn's local airport, PHX, are straightforward; others are more obscure or random.
Visit their website to browse codes from more than 200 airports around the world. Here's a sample:
ARN
Stockholm Arlanda Airport, Stockholm
Stockholm's airport is named ARlaNda, a made-up word combining Arland, another name for the nearby parish of Ärlinghundra, and landa, the Swedish verb meaning "to land."
Stockholm Arlanda Airport, Stockholm
Stockholm's airport is named ARlaNda, a made-up word combining Arland, another name for the nearby parish of Ärlinghundra, and landa, the Swedish verb meaning "to land."
CDG
Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris
Renamed and officially opened in 1974, France's largest airport is named after Charles De Gaulle, former president and founder of the French Fifth Republic.
Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport, Paris
Renamed and officially opened in 1974, France's largest airport is named after Charles De Gaulle, former president and founder of the French Fifth Republic.
CGK
Soekarno–Hatta International Airport, Jakarta, Indonesia
Soekarno–Hatta International serves the capital city of Jakarta and honors Indonesia's first president and first vice president. It receives its code from the CenGKareng district in the city of Tangerang, where it's located.
Soekarno–Hatta International Airport, Jakarta, Indonesia
Soekarno–Hatta International serves the capital city of Jakarta and honors Indonesia's first president and first vice president. It receives its code from the CenGKareng district in the city of Tangerang, where it's located.
CVG
Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport, Cincinnati
Serving the greater Cincinnati metro area, Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky's airport code comes from the nearby city of CoVinGton.
Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport, Cincinnati
Serving the greater Cincinnati metro area, Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky's airport code comes from the nearby city of CoVinGton.
DXB
Dubai International Airport, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
When Dubai International opened in 1960, the airport code DUB was already in use by Dublin. DuBai subbed an X for the U, making its unique airport code of DXB.
Dubai International Airport, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
When Dubai International opened in 1960, the airport code DUB was already in use by Dublin. DuBai subbed an X for the U, making its unique airport code of DXB.
EWR
Liberty International Airport, Newark, New Jersey
When airport codes switched from two letters to three, the Navy reserved all codes starting with N. NEWaRk, then, used the other letters in its name to make EWR.
Liberty International Airport, Newark, New Jersey
When airport codes switched from two letters to three, the Navy reserved all codes starting with N. NEWaRk, then, used the other letters in its name to make EWR.
 Via Wikimedia CommonsStockholm Arlanda Airport
Via Wikimedia CommonsStockholm Arlanda Airport
IAD
Dulles International Airport, Washington, D.C.
Dulles International Airport's three-letter code was once DIA. When handwritten, it was often misread as DCA, another Washington airport. It was reversed to IAD to avoid confusion.
Dulles International Airport, Washington, D.C.
Dulles International Airport's three-letter code was once DIA. When handwritten, it was often misread as DCA, another Washington airport. It was reversed to IAD to avoid confusion.
LAX
Los Angeles International Airport, Los Angeles
Before the 1930s, airports had two-letter codes. When codes switched to three letters, many added the letter X to the end. LA (Los Angeles) became LAX. (See also:PDX.)
Los Angeles International Airport, Los Angeles
Before the 1930s, airports had two-letter codes. When codes switched to three letters, many added the letter X to the end. LA (Los Angeles) became LAX. (See also:PDX.)
LHR
London Heathrow Airport, London
London HeathRow takes its name from Heathrow, a hamlet northwest of where the then-small airfield was started in 1929.
London Heathrow Airport, London
London HeathRow takes its name from Heathrow, a hamlet northwest of where the then-small airfield was started in 1929.
OGG
Kahului Airport, Kahului, Hawaii
Kahului Airport is named after its home city, but its airport code honors Hawaiian-born pilot Bertram J. HOGG.
Kahului Airport, Kahului, Hawaii
Kahului Airport is named after its home city, but its airport code honors Hawaiian-born pilot Bertram J. HOGG.
ORD
O'Hare International Airport, Chicago
Before the airport was renamed after Medal of Honor recipient Edward O'Hare in 1949, it was known as ORcharD Field Airport.
O'Hare International Airport, Chicago
Before the airport was renamed after Medal of Honor recipient Edward O'Hare in 1949, it was known as ORcharD Field Airport.
SFO
San Francisco International Airport, San Francisco
When codes switched to three letters from two, many added the letter X to the end.San FranciscO instead used its last letter O.
San Francisco International Airport, San Francisco
When codes switched to three letters from two, many added the letter X to the end.San FranciscO instead used its last letter O.
SUX
Sioux Gateway Airport, Sioux City, Iowa
SioUX City petitioned twice to have its airport code, SUX, changed. With no great alternatives, it stuck with it and now uses the slogan "Fly SUX."
Sioux Gateway Airport, Sioux City, Iowa
SioUX City petitioned twice to have its airport code, SUX, changed. With no great alternatives, it stuck with it and now uses the slogan "Fly SUX."
UIO
Mariscal Sucre International Airport, Quito, Ecuador
Mariscal Sucre International is named after Antonio José de Sucre, who fought for the independence of Quito, in what is now Ecuador. Because the Federal Communications Commission reserved codes starting with Q, it opted for other letters from its home city of QUItO.
Mariscal Sucre International Airport, Quito, Ecuador
Mariscal Sucre International is named after Antonio José de Sucre, who fought for the independence of Quito, in what is now Ecuador. Because the Federal Communications Commission reserved codes starting with Q, it opted for other letters from its home city of QUItO.
YYZ
Pearson International Airport, Toronto
Airport codes starting with Y designate Canadian airports. The YZ isn't as clear but is said to be the old railway station code for Malton, an area west of Toronto where the airport is located.
Pearson International Airport, Toronto
Airport codes starting with Y designate Canadian airports. The YZ isn't as clear but is said to be the old railway station code for Malton, an area west of Toronto where the airport is located.
For more airport codes and their origin stories, visit airportcod.es.
Nick Crohn is a senior JavaScript developer living in Chandler, Arizona.
Lynn Fisher is an artist and designer who lives in Chandler, Arizona.
Read more: http://www.slate.com/articles/technology/technology/2015/03/airport_abbreviations_how_los_angeles_became_lax_and_dulles_iad.html#ixzz3VrhrZzhW
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)